Plants
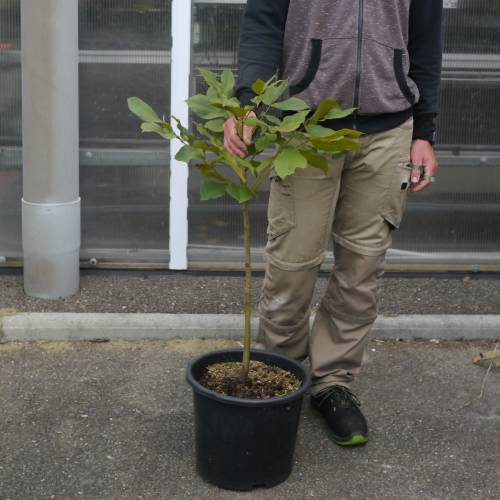
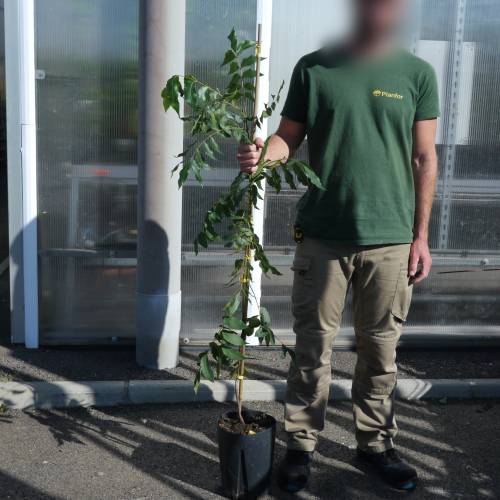
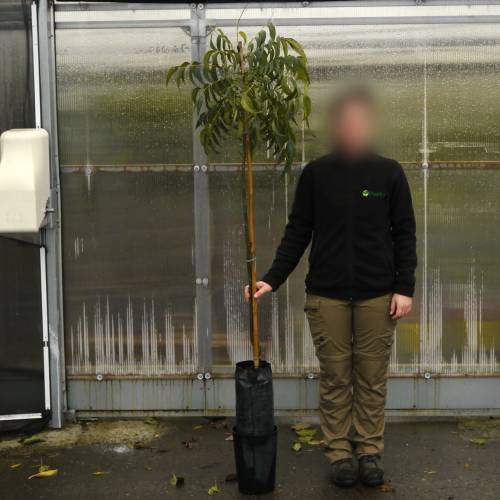
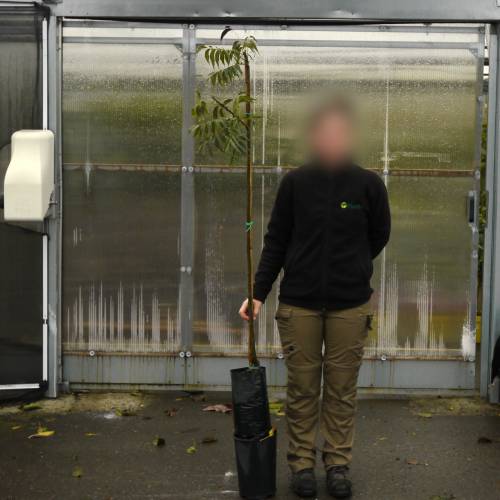
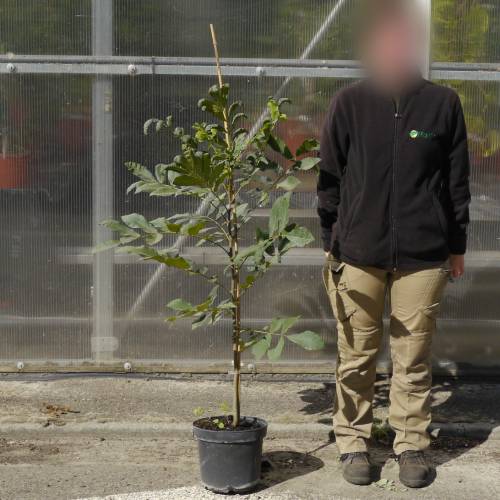
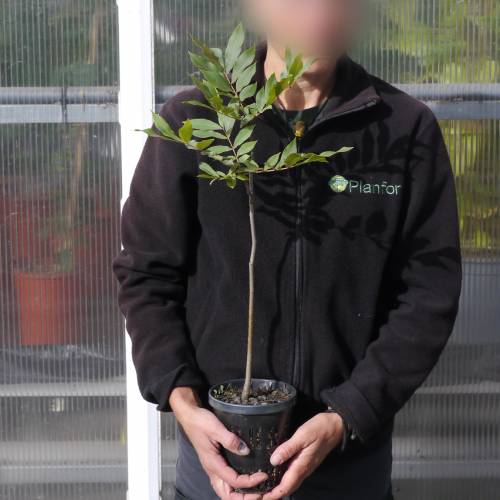
Pecan tree / Carya illinoinensis
-
102.26 € Pecan tree 'Choctaw' (Carya illinoinensis)
7840U - Available
-
102.26 € Pecan tree 'Delmas' (Carya illinoinensis)
7840W - Available
-
86.02 € Pecan tree 'Pawnee' (Carya illinoinensis)
7804D - Available
-
86.02 € Pecan tree 'Wichita' (Carya illinoinensis)
7804E - Available
-
69.79 € Pecan tree (Carya illinoinensis)
7804SX - Available
-
67.03 € Pecan tree (Carya illinoinensis)
7804TX - Available
-
7.75 € Pecan tree (Carya illinoinensis)
7804J7 - Available
-
7.23 € Pecan tree (Carya illinoinensis)
7804J8 - Available
-
6.71 € Pecan tree (Carya illinoinensis)
7804J9 - Available
-
6.19 € Pecan tree (Carya illinoinensis)
7804K1 - Available
-
5.67 € Pecan tree (Carya illinoinensis)
7804K2 - Available
-
5.15 € Pecan tree (Carya illinoinensis)
7804K3 - Available
-
0.40 € FERTILISER
7804A - Available
-
Geographic origin: North America
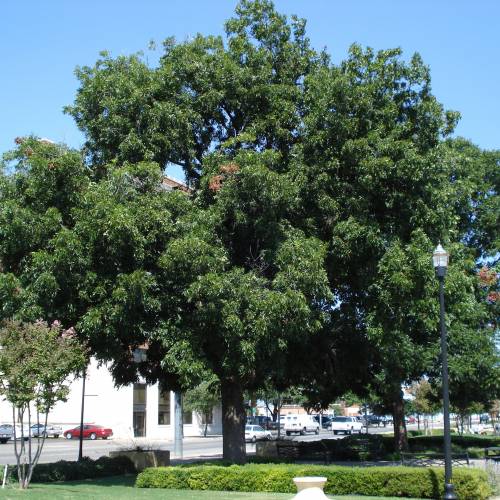
Adult size: Height up to 25 m, width up to 10 m
Foliage: Deciduous.
Type of soil: Light and humus rich, acidic to neutral
Climate: Hardy to -15°C.
Position: partial shade to full sun.
Properties and uses:
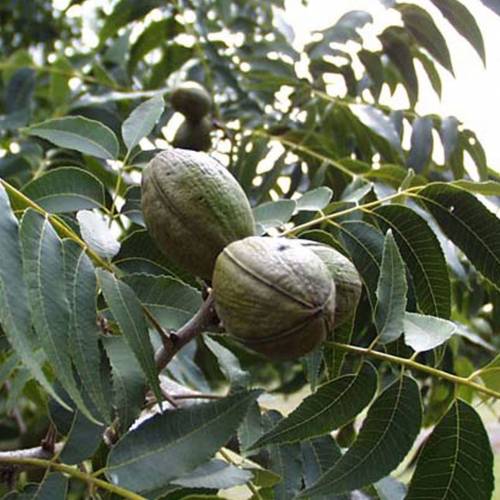
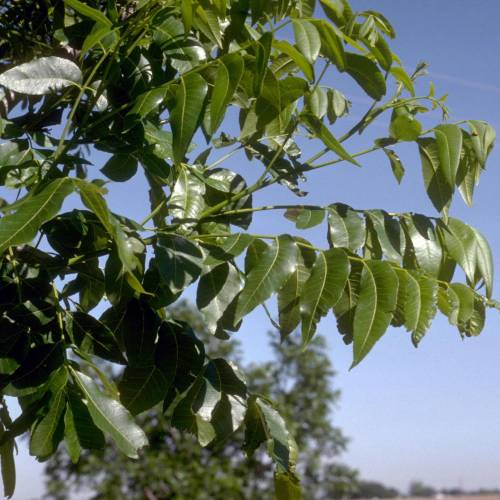
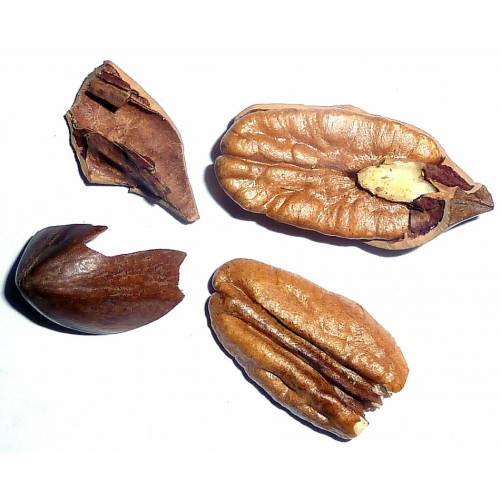
The Pecan tree is mostly cultivated for its nuts. The innate, green and glossy leaves have long lance-shaped leaflets. They turn yellow in autumn.
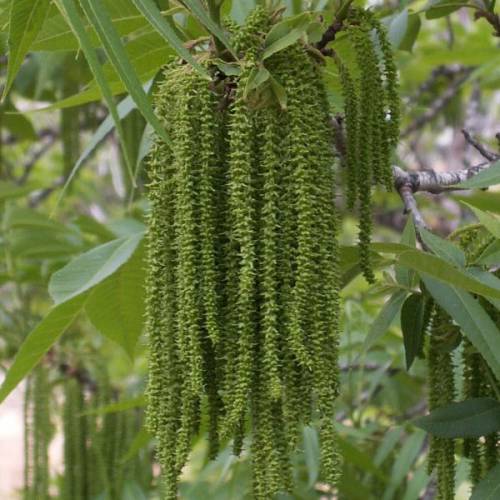
The blossoms appear before the leaves, at the end of the winter. First, the 18-cm male catkins decorate the branches followed by the inconspicuous female blossoms.
The Pecan trees do only a poor job of self-pollination, so it is best to plant several trees together to obtain some nuts.
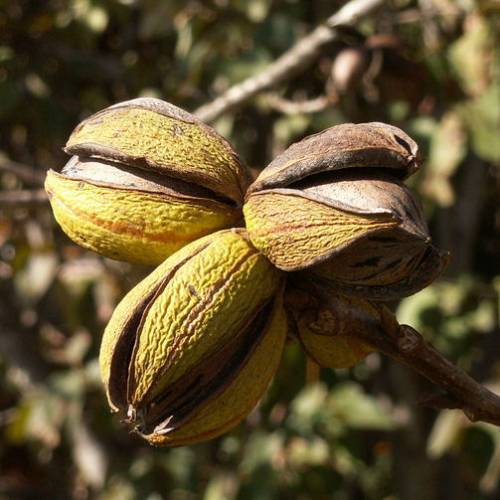
The trees planted around the Mediterranean Sea are the only ones to provide pecan nuts which are harvested in autumn. Properly cured nuts may keep several months in a cool, dry and well-ventilated location.
With its round and broad crown, the Pecan Tree can be planted alone. The tree can also tolerate a lot of moisture for a while and so can help restore a healthy riverbank.
Plant them now: the shortest way to your plate is through your garden!
Several cultivars exist:
- Pecan tree 'Cheyenne': Self-fertile late variety, very good production
- Pecan tree 'Choctaw': Late variety (group B), partially self-fertile, pollination is improved with the planting of a group A pecan tree.
- Pecan tree 'Mohawk': Late variety (group B), partially self-fertile, pollination is improved with the planting of a group A pecan tree.
- Pecan tree 'Delmas': Early variety (group A), partially self-fertile, pollination is improved with the planting of a group B pecan tree.
- Pecan tree 'Pawnee': Early variety (group A), partially self-fertile, pollination is improved with the planting of a group B pecan tree.
- Pecan tree 'Wichita': Early variety (group B), partially self-fertile, pollination is improved with the planting of a group A pecan tree. -
-

Christmas : Our selection of plants
201 products -

Edible Wild fruits
93 products -

Fruit Trees
114 products -

New Plants
416 products -

Nuts
12 products -

Plants for agroforestry
121 products -

Rare Plants
247 products -

Riparian forest
83 products -

Shade trees
51 products -

Trees, Mature Trees
154 products -

Trees of Fall Interest
63 products -

Tree species of the future
9 products -

Walnut
3 products
-














